Satellite IoT modules are transforming the way companies interact with their customers, increase operational efficiency, and gain insights into their business operations. Delivering truly global, reliable coverage, these modules enable organisations to unlock the full potential of the Internet of Things (IoT).
The latest research from IoT Analytics estimates that by the end of 2023, the IoT will be responsible for 16 billion active devices. But given the importance of reliable connectivity, how many of these devices will be satellite-enabled?
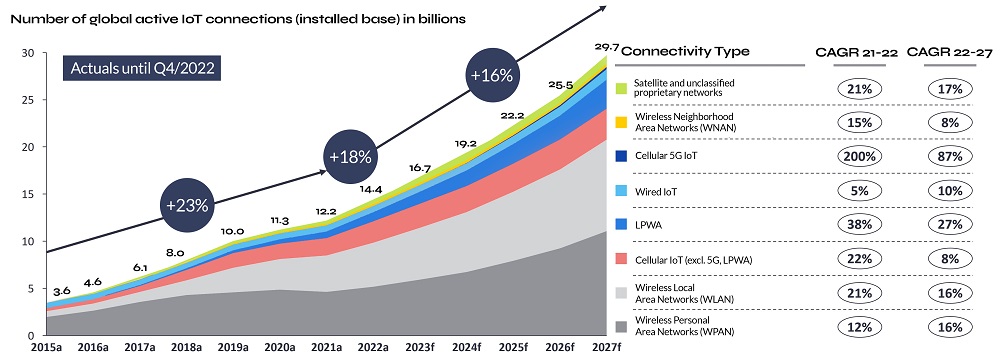
Source: IoT Analytics Research, State of IoT 2023
Note from authors: IoT connections do not include any computers, laptops, fixed phone, cellphones, or consumers’ tablets. Counted are active nodes/devices or gateways that concentrate the end-sensors, not every sensor/actuator. Simple one-directional communications technology not considered (e.g. RFID, NFC). Wired includes ethernet and fieldbuses (e.g. connected industrial PLCs or I/O modules); Cellular includes 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G; LPWA includes unlicensed low-power networks; WPAN includes Bluetooth, Zigbee, Z-Wave or similar, WLAN includes Wi-Fi and related protocols; WNAN includes non-short-range mesh, such as Wi-SUN; Unclassified proprietary networks include any range.
As you might expect, IoT connectivity continues to be dominated by Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and cellular IoT. But interestingly, the CAGR for each of these is predicted to decrease, in some cases significantly (cellular from 200% to 87%) by 2027. In contrast, satellite IoT connections are projected to grow from 6 million to 22 million (at a CAGR of 25%).
What are satellite IoT modules?
Satellite IoT modules or modems are specialised hardware components that enable devices to communicate with satellites and access global connectivity. These modules are designed to be power-efficient, compact, and compatible with existing IoT device architectures. Typically they are used in areas of IoT networks where traditional cellular networks or other forms of terrestrial connectivity are either unavailable or unreliable, such as remote or rural areas.
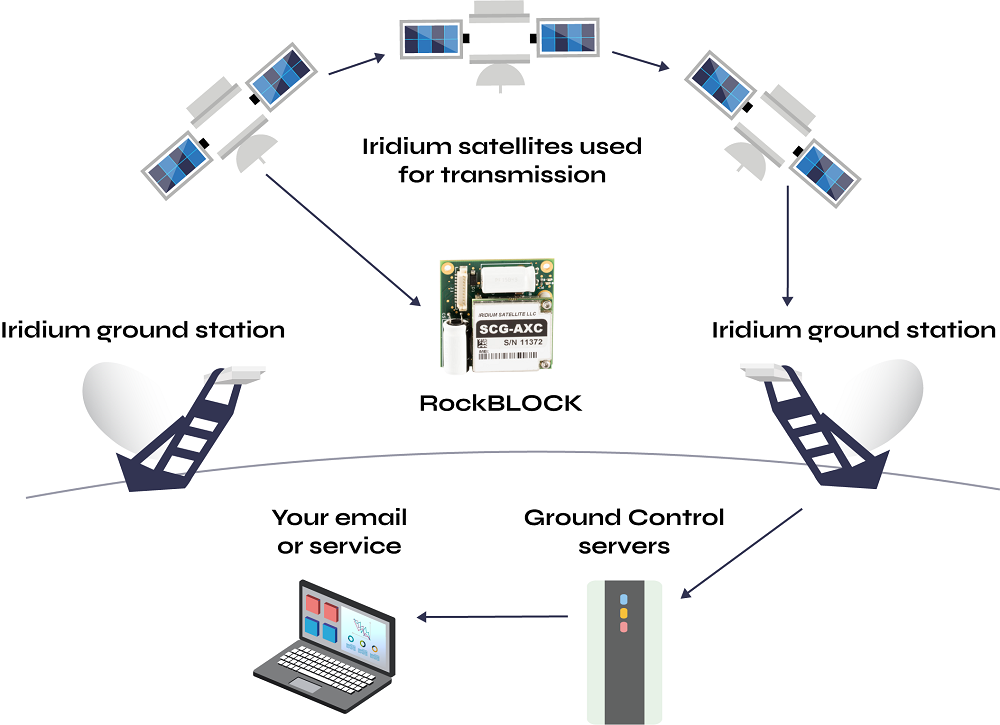
How do they work?
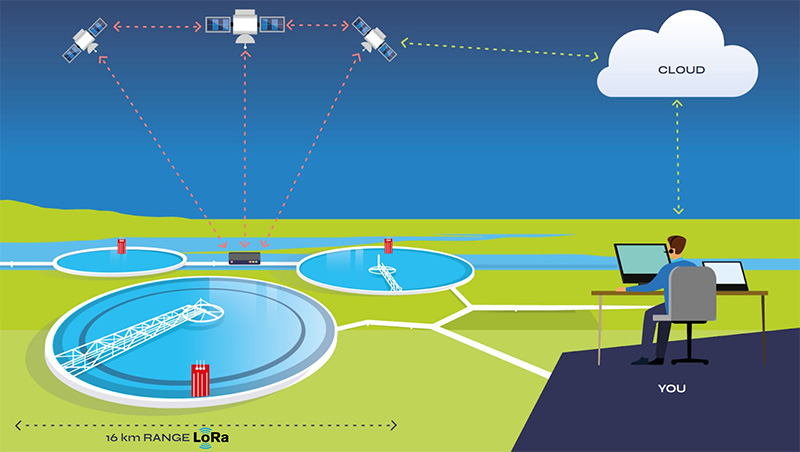
Simply, satellite IoT modules work by leveraging satellite networks to establish communication between IoT devices and the central infrastructure.
IoT devices such as sensors or trackers are equipped with satellite modems (e.g. the RockBLOCK) that transmit data to satellites orbiting the Earth. Data is sent to a satellite, in this case a satellite within Iridium’s constellation, the satellite then relays the received data down to the ground station.
The ground station serves as a gateway to bridge the communication between the satellite and the Network Operations Centre (NOC), forwarding the data on to the appropriate destination. This can be a cloud platform, a server, or any designated system that collects and manages the IoT data.
How do satellite and terrestrial IoT modules compare?
Terrestrial and satellite IoT modules share many similarities. They both offer the necessary connectivity and processing power for devices to exchange data and come in multiple form factors depending on the deployment requirements. From PCBs intended to be built-in to the sensor array, to fully ruggedised and waterproof devices with integrated processing, storage and security features.
What’s more, all IoT modems require an antenna, the size of which will depend on the signal strength needed. Satellite IoT devices can have surprisingly small antennas if the orbiting satellite service operates in a high frequency, like Iridium (see the patch antenna on the RockBLOCK 9603, which measures just 25 x 25 x 4mm). Other satellite network operators leverage lower frequencies, which require larger, external antennas – Swarm, for example, needs a 20cm antenna to communicate with its satellites.
Terrestrial and satellite IoT modules also exhibit distinct differences that set them apart:
Further benefits to Satellite IoT
SECURITY AND DATA PRIVACY
Satellite IoT networks employ robust security measures to protect data transmission and ensure privacy. Encryption and authentication protocols are implemented to safeguard data integrity and prevent unauthorised access. Firewalls and VPNs are leveraged when data travels over public infrastructure like the internet, but this can be completely circumnavigated with either private lines or a private satellite network like TSAT.

RELIABLE AND RESILIENT
Satellite networks are designed to be highly reliable and resilient. They are less susceptible to environmental factors, natural disasters, or infrastructure failures that can disrupt terrestrial networks. Typically offering high reliability and uptime, satellite IoT ensures consistent data transmission and device communication even in challenging and remote environments.
SCALABILITY
Satellite IoT networks offer scalability to accommodate a large number of connected devices. Businesses can scale their IoT deployments without concerns about network capacity limitations or infrastructure upgrades. This scalability is crucial for projects that require the connection of a large number of sensors, devices, or assets spread across vast areas.

RAPID DEPLOYMENT
Satellite IoT modules enable rapid deployment, especially in remote or temporary setups. They eliminate the need for building new terrestrial infrastructure or relying on existing networks. Companies can quickly establish IoT connectivity in remote or disaster-stricken areas, facilitating faster response times and data collection.

The Future of IoT modules
The previously mentioned research from IoT Analytics, also noted that the integration of satellite connectivity options into LPWA chipsets, spearheaded by companies like Qualcomm, has the potential to accelerate the adoption of hybrid IoT devices. Sony Semiconductor has already introduced ALT1350, the first cellular IoT LPWA chipset with satellite connectivity, expanding the communication capabilities of IoT devices beyond conventional network limitations. This significant development paves the way for new possibilities in the IoT landscape. By incorporating satellite connectivity into LPWA chipsets, further innovation and growth are projected. Until then however, the combination of satellite and terrestrial networks still delivers organisations the flexibility to realise the full potential of their IoT deployments.
Choosing the right Satellite IoT modules
The majority of satellite IoT modules are proprietary technology. Simply, they are designed to leverage a specific satellite network, for example, Viasat, and often a specific airtime service, for instance, IoT Pro. As each satellite network offers different coverage, reliability, latency and so on, and each service allows different data rates, message sizes and more, its key companies evaluate their connectivity needs thoroughly. Satellite connectivity can be expensive (see our post on how to reduce satellite connectivity costs), so typically businesses will only use this for areas of their IoT network where they are struggling with connectivity, or for the purposes of failover or backhaul. In any case, businesses should assess their data transmission requirements and select the most appropriate satellite airtime service for their application, before considering their hardware options.
If you do have any specific queries related to airtime, please don’t hesitate to get in touch. We’ve been doing this for over 20 years and though we have significant relationships with both Iridium and Inmarsat we’re not tied to any one provider, just helping you find the best solution for your project and budget.
Comparing popular Satellite IoT devices and airtime services
|
|
|||
|
Service Provider:
|
Iridium
|
Iridium
|
Viasat
|
|
Connection Type:*
|
Messaging-based
|
IP-based service
|
IP-based service
|
|
Data Speeds:
|
n/a*
|
22 Kbps up, 88 Kbps down
|
448 Kbps up, 464 Kbps down
|
|
Response Time:
|
<1 second
|
<1 second
|
<2 seconds
|
|
Coverage:
|
Global
|
Global
|
Global, exc. polar region
|
|
Power Efficiency:
|
Very high
|
High
|
High
|
|
Ideal Applications: |
|
|
|
|
Service Provider:
|
Iridium
Short Burst Data (SBD) Products
|
Iridium
Iridium Certus 100 Devices
|
Viasat
IoT Pro Terminals
|
Once companies have selected their preferred airtime service, it’s important to consider the interfaces and integration options provided by the satellite IoT modules. It is important to determine if the modules support the necessary interfaces (e.g., UART, SPI, I2C) for seamless connectivity with IoT devices or sensors. Additionally, assessing compatibility with standard IoT protocols (e.g., MQTT, HTTP) is vital to ensure smooth integration within your existing IoT infrastructure.
Another aspect that businesses need to assess is the size and form factor of the satellite IoT modules. Consider any space limitations, weight restrictions, and physical constraints that may be relevant. For instance, if your application requires burying sensors or housing them within an enclosure, antenna options must be considered. Depending on factors such as the enclosure material, an external antenna may be required to enhance signal strength. This improves communication reliability and can help facilitate clear line-of-sight with geostationary satellite networks.
Moreover, companies must verify that the satellite IoT modems comply with relevant certifications and regulatory standards applicable to their target markets. Compliance with certifications like FCC, CE, and RoHS ensures adherence to quality, safety, and environmental standards. For those with deployments spanning larger geographical areas, it’s prudent to ensure that there are no local restrictions for satellite connectivity; some countries such as India restrict use without prior government approval.
Additionally, it is important to assess the cost considerations associated with the satellite IoT modules. This includes evaluating module pricing, airtime costs, and any additional fees or licensing requirements. Considering the total cost of ownership over the desired lifespan of the IoT project will provide a comprehensive understanding of the financial implications.
Finally, though satellite IoT modules are designed to be power efficient, it is necessary to evaluate power consumption. Depending on the deployment scenario, it might be worthwhile to consider modules that can leverage alternative power sources such as solar power, like the Iridium Edge Solar.
By carefully considering these factors, companies can make informed decisions when selecting satellite IoT modules, ensuring optimal integration, performance, and cost-effectiveness for their specific IoT projects.
Overall, satellite connectivity is a game-changer for IoT, enabling devices to operate in previously unreachable areas and opening up new possibilities for businesses and industries. By choosing the right satellite IoT module and airtime service, businesses can unlock the full potential of IoT and drive innovation in their respective fields.
Unlimit your IoT deployment today
Don't let geographical limitations hold back your IoT ambitions. Let our team of experts guide you towards achieving your goals. Fill in the form below and take the next step towards unlocking the full potential of your IoT project.